Aptitude
HCF & LCM
-
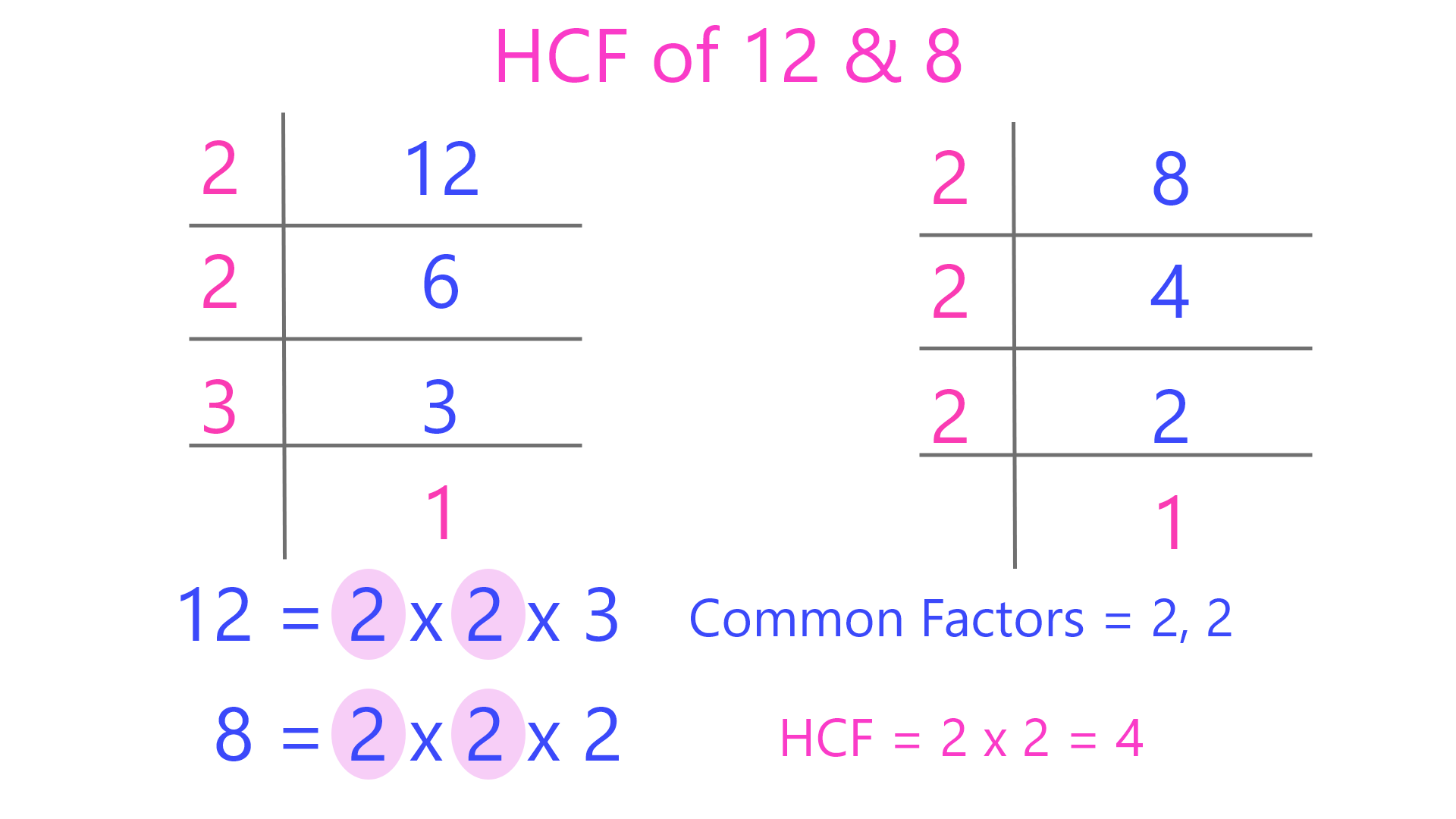
HCF (Highest Common Factor) of two or more integers is the largest positive integer that divides each of them exactly.
It is also called GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) or GCF (Greatest Common Factor). We denote it as HCF(x, y) or GCD(x, y).
Use cases: simplifying fractions, solving problems on ratios, and finding common divisors in divisibility problems.
-
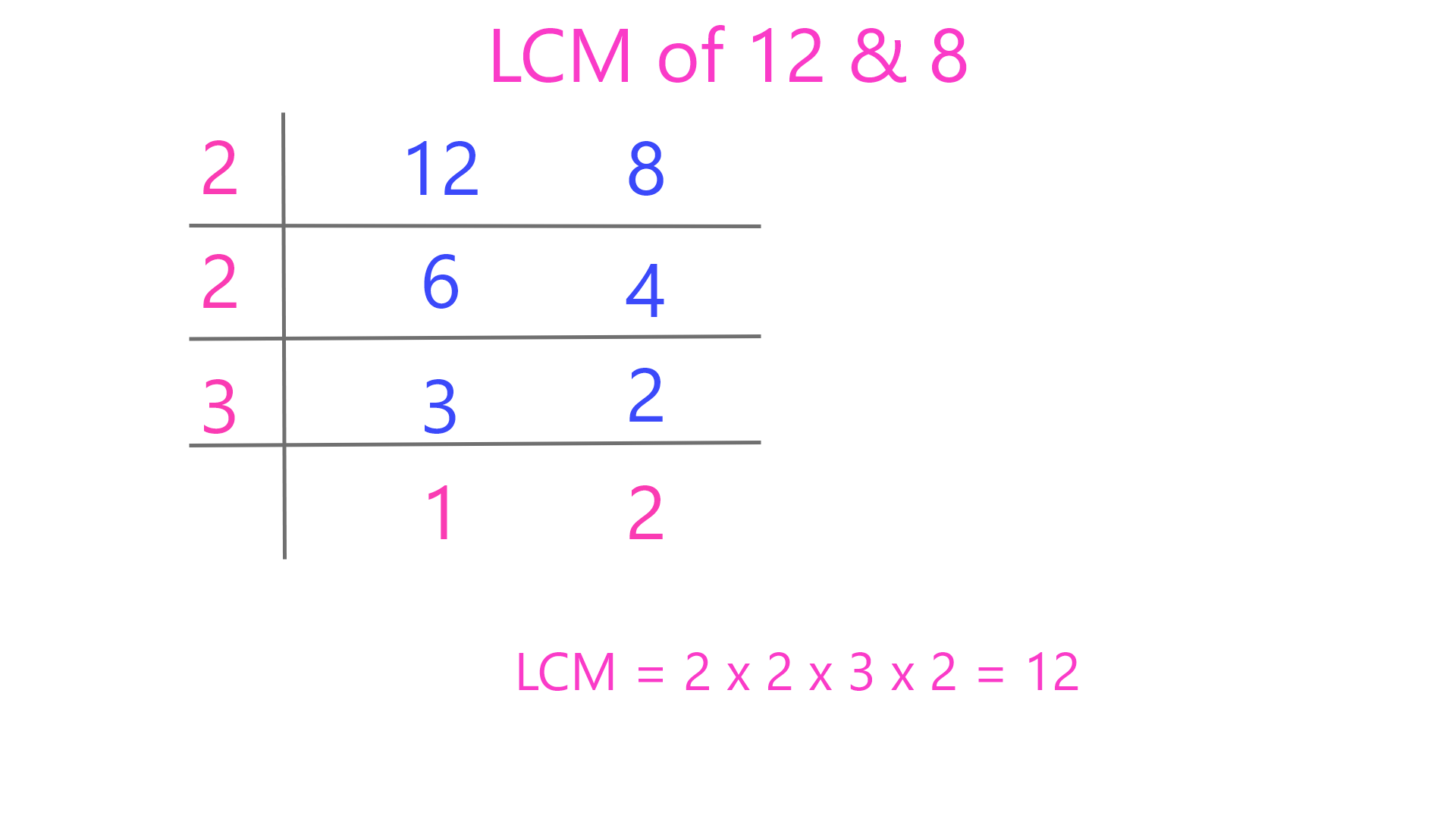
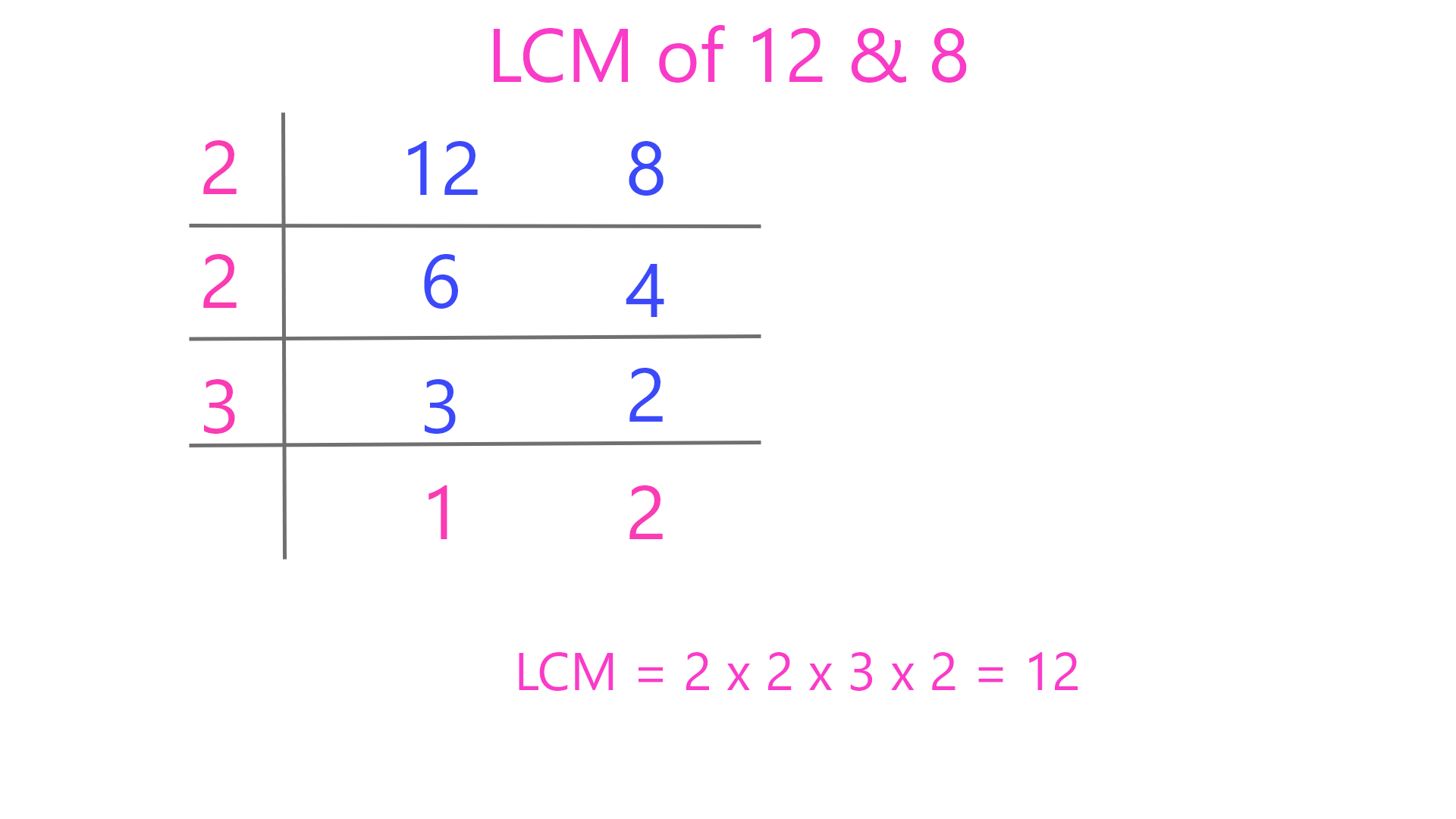
LCM (Least Common Multiple) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of each of them.
-
LCM is useful for adding/subtracting fractions, synchronizing repeating cycles, and scheduling problems.
You can compute LCM by several methods; the common ones are listed below.
-
The common multiple method finds the LCM by listing multiples of each number and picking the smallest common one.
Steps:
- List multiples of each given number.
- Identify the common multiples from the lists.
- The smallest common multiple is the LCM.
Note: This method is straightforward but can be inefficient for large numbers.
-
The prime factorization method uses prime factors to compute both HCF and LCM efficiently.
Steps to find LCM using prime factors:
- Express each number as a product of primes.
- For LCM, take each prime with the highest exponent appearing in any factorization.
- Multiply these chosen prime powers — the result is the LCM.
For HCF (GCD) using factors, take each prime with the lowest exponent common to all numbers and multiply them.


-
The ladder (division) method is a visual prime-division technique useful for finding LCM of many numbers at once.
Steps:
- Write the numbers side by side inside an "L" frame.
- Divide all numbers by a prime that divides at least one of them and write the quotients below.
- Repeat with prime divisors until all entries become 1.
- LCM = product of all prime divisors used × final 1s (i.e. multiply all numbers outside and inside the ladder).
Tip: Always divide by primes and simplify as you go to avoid mistakes.